Sommaire de la page
Thématique de recherche
Notre équipe concentre ses activités de recherche sur les réponses immunitaires anormalement dirigées contre les propres tissus de l’organisme dans les maladies auto-immunes, principalement sur le lupus érythémateux disséminé (LED), et sur la découverte de nouvelles molécules médicamenteuses conçues pour immunoréguler spécifiquement ces maladies.
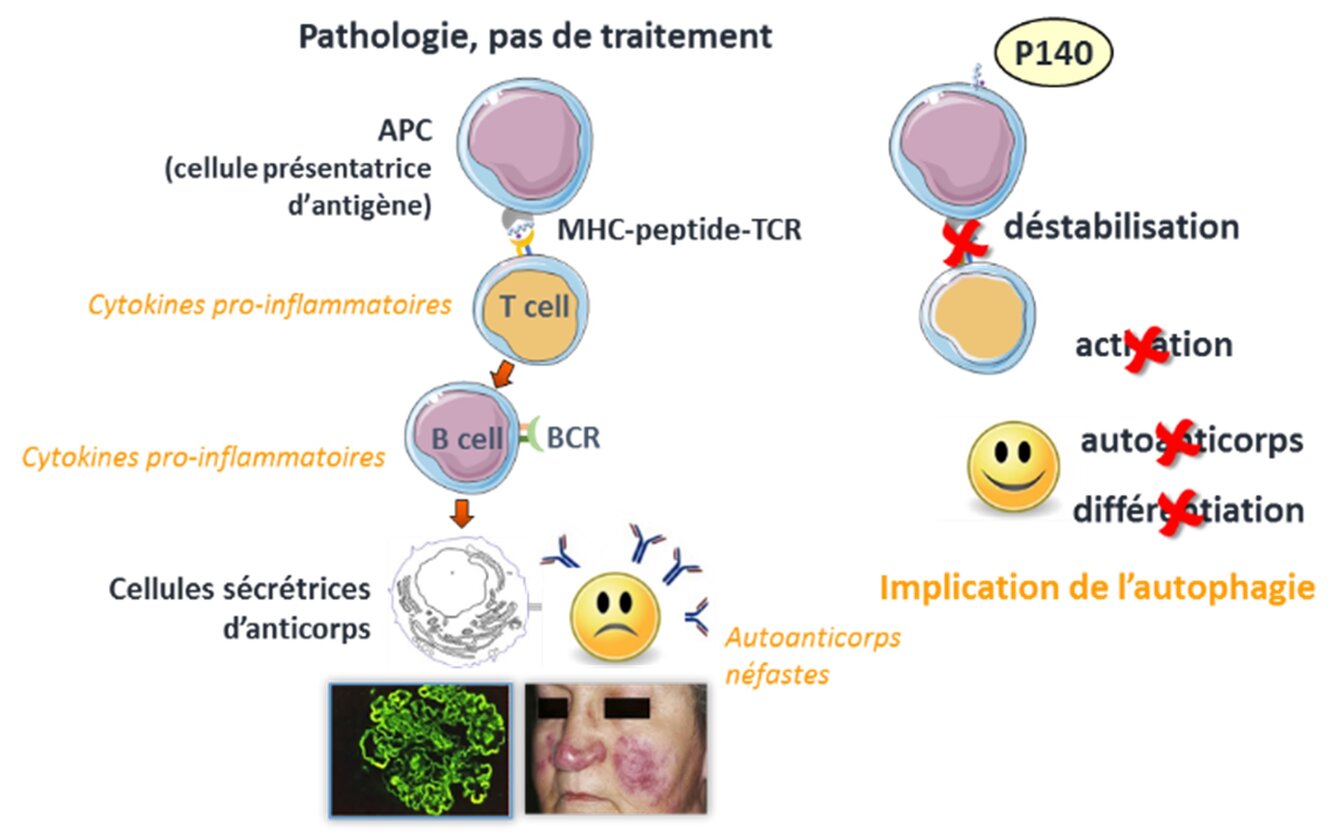
Le LED est une maladie chronique multigénique dont l'étiologie reste largement inconnue. Si l'utilisation de corticostéroïdes et d'immunosuppresseurs a permis de fournir de bien meilleurs soins aux patients, ces médicaments ont des effets secondaires délétères, des contre-indications et une certaine toxicité qui peuvent contribuer à la morbidité de la maladie. Il y a quelques années, notre groupe a découvert un phosphopeptide, appelé P140, qui présente des effets protecteurs chez les souris MRL/lpr qui développent une maladie proche du LED. Dans une étude de phase IIb multicentrique, randomisée et contrôlée par placebo, P140/LupuzorTM s'est avéré dépourvu d’effets secondaires et a atteint ses principaux objectifs d'efficacité, confirmant ainsi les données précliniques obtenues chez les souris lupiques. Il fait actuellement l'objet d'essais cliniques de phase III.
Le peptide P140 se lie à la protéine chaperonne HSPA8/HSC70 et diminue son expression, dont nous avons découvert qu'elle était accrue dans les cas de lupus. Cette interaction, démontrée à la fois in vitro et in vivo, déstabilise la liaison de HSPA8 à d'autres protéine chaperonnes et affecte son activité biologique. Administré à des souris MRL/lpr, le P140 réduit le flux autophagique hyperactivé dans les cellules B présentatrices d'antigènes, avec une accumulation de marqueurs de macroautophagie et un blocage du processus d'autophagie excessif médié par les chaperonnes (CMA). Chez les souris et les patients atteints de lupus, le P140 corrige un certain nombre de défauts des lysosomes que nous avons découverts et diminue l'expression anormalement élevée des molécules du complexe majeur d'histocompatibilité (CMH). Tous ces effets contribuent à réduire l'hyperactivation de l'autoréactivité des cellules T et B et, in fine, la production d'auto-anticorps pathogènes qui se déposent dans les tissus en créant un état d’inflammation douloureux. Le P140 a démontré des effets bénéfiques dans des modèles animaux imitant d'autres maladies inflammatoires aussi diverses que la maladie de Sjögren, les maladies inflammatoires de l'intestin (MICI), la parodontite, la goutte et l'asthme.
Nos études en cours sont particulièrement axées:
Au niveau cellulaire et moléculaire, sur les processus d'autophagie lysosomale qui apparaissent anormaux dans les conditions inflammatoires et s'avèrent être des points chauds décisifs dans la pathologie des conditions inflammatoires aiguës et chroniques.
Au niveau physiopathologique, dans le lupus et d'autres modèles d'inflammation, sur les altérations cliniques qui émergent progressivement, y compris les altérations du microbiome, en relation avec les défauts d'autophagie.
Plus largement, sur les stratégies peptidiques développées dans le but de moduler spécifiquement l'autoréactivité, restaurer la tolérance immunitaire et inverser le cours des maladies dans des modèles murins de pathologies inflammatoires chroniques, y compris les maladies neurologiques/neurodégénératives et métaboliques (MASH, obésité). L'accent est mis sur le possible effet abscopal dans le mode d'action du P140.
En parallèle, nous développons des stratégies innovantes pour administrer des peptides thérapeutiques de manière non invasive en utilisant diverses nanostructures pour leur délivrance. Des efforts seront également consacrés aux questions de théranostic avec le développement de puces spécifiques pour identifier les répondeurs des non-répondeurs au traitement peptidique, et de suivi des peptides à l'aide de nouvelles méthodes d'imagerie sur individus vivants.
Contact
L'équipe est basée dans les locaux de l'Institut de Science et d'Ingénierie Supramoléculaires (ISIS), 8 Allée Gaspard Monge, 67000 Strasbourg.
Pr Sylviane Muller
Pr Philippe Georgel
Soutiens financiers

Membres de l'équipe
El Kaakour Lara
- Bureau : ISIS / Reims URCA 7369 MEDyC
- lelkaakour[at]unistra.fr
- Bureau : ISIS / 230
- pgeorgel[at]unistra.fr
- Bureau : ISIS / 406
- hdavid[at]unistra.fr
- Bureau : ISIS / 231
- joffrey.mary[at]etu.unistra.fr
- Bureau : ISIS / 231
- dylan.mastrippolito[at]etu.unistra.fr
- Bureau : ISIS / 206
- sylviane.muller[at]unistra.fr
- Bureau : ISIS / 230
- talamini[at]unistra.fr
- Bureau : ISIS / 231
- cverdot[at]unistra.fr
Publications
Brady S, Poulton J, Muller S (2024). Inclusion body myositis: Correcting mitochondfrial and lysosomal autophagy impairment as a potential therapeutic strategy. Autoimmun Rev 19:103644. doi: 10.1016/j.autrev.2024.103644.
Maujean T, Ramanoudjame SM, Riché S, Le Guen C, Boisson F, Muller S, Bonnet D, Gulea M, Marchand P (2024). Hetero-Diels-Alder and CuAAC Click Reactions for Fluorine-18 Labeling of Peptides: Automation and Comparative Study of the Two Methods. Molecules 29(13):3198. doi: 10.3390/molecules29133198.
Rafiq S, Mungure I, Banz Y, Niklaus NJ, Kaufmann T, Müller S, Jacquel A, Robert G, Auberger P, Torbett BE, Muller S, Tschan MP, Humbert M (2024). HSPA8 Chaperone Complex Drives Chaperone-Mediated Autophagy Regulation in Acute Promyelocytic Leukemia Cell Differentiation. Pharmacology 109(4):216-230. doi: 10.1159/000537864.
Bonam SR, Mastrippolito D, Georgel P, Muller S (2024). Pharmacological targets at the lysosomal autophagy-NLRP3 inflammasome crossroads. Trends Pharmacol Sci 45(1):81-101. doi: 10.1016/j.tips.2023.11.005.
Lasalo M, Jauffrais T, Georgel P, Matsui M (2024). Marine Microorganism Molecules as Potential Anti-Inflammatory Therapeutics. Mar Drugs 22(9):405. doi: 10.3390/md22090405.
Adiguzel Y, Mahroum N, Muller S, Blank M, Halpert G, Shoenfeld Y (2023). Shared Pathogenicity Features and Sequences between EBV, SARS-CoV-2, and HLA Class I Molecule-binding Motifs with a Potential Role in Autoimmunity. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol 65:206-230. doi: 10.1007/s12016-023-08962-4.
Renaudineau Y, Muller S, Hedrich CM, Chauveau D, Belliere J, De Almeida S, Damoiseaux J, Scherlinger M, Guery JC, Sailler L, Bost C (2023). Immunological and translational key challenges in systemic lupus erythematosus: a symposium update. J Transl Autoimmun 6:100199. doi: 10.1016/j.jtauto.2023.100199.
Muller S (2023). The abscopal effect: Implications for drug discovery in autoimmunity. Autoimmun Rev 22:103315. doi: 10.1016/j.autrev.2023.103315.
Jacotot E, Talamini L, Bonam SR, Vieira AT, Fremeaux-Bacchi V, Radic M, Dragon-Durey MA, Lozano JM, Saia RS, Muller S (2023). Innate immune responses in COVID-19. In Autoimmunity, COVID-19, Post-COVID19 syndrome and COVID-19 vaccination, 1st Edition (Eds: Shoenfeld Y, Dotan A); chapter 3 pages 63-128. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-443-18566-3.00041-4.
Dotan A, Kanduc D, Muller S, Shoenfeld Y (2023). SARS-CoV-2, fertility-related autoantibodies and reproductive injury. In Autoimmunity, COVID-19, Post-COVID19 syndrome and COVID-19 vaccination, 1st Edition (Eds: Shoenfeld Y, Dotan A); chapter 29 pages 595-601. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-443-18566-3.00024-4.
Gros F, Muller S (2023). The role of lysosomes in metabolic and autoimmune diseases. Nat Rev Nephrol 19(6):366-383. doi: 10.1038/s41581-023-00692-2.
Lozano JM, Muller S (2023). Monkeypox: Potential vaccine development strategies. Trends Pharmacol Sci 44:15-19. doi: 10.1016/j.tips.2022.10.005.
Georgel P, Lebouvier N, Matsui M (2023). Editorial: Exploring the unique biodiversity of the Western Pacific to identify novel anti-infectious and anti-inflammatory compounds of natural origin. Front Pharmacol 14:1154627. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1154627.
Lathuillère C, Georgel P (2023). Recent progresses in innate neuro-immunology hold great promises for the management of inflammatory diseases. Brain Behavior and Immunity Integrative Volume 2, 100005. doi: 10.1016/j.bbii.2023.100005.
De Cauwer A, Pichot A, Molitor A, Stemmelen T, Carapito R, Bahram S, Georgel P (2023). Measuring the transcriptome-wide effects of aging on murine adipocytes using RNAseq. STAR Protoc 4(3):102397. doi: 10.1016/j.xpro.2023.102397.
Brun S, De Sèze J & Muller S (2022). CIDP: Current treatments and identification of targets for future specific therapeutic intervention. Immuno 2:118-131. doi: 10.3390/immuno2010009.
Galvão I, Mastrippolito D, Talamini L, Aganetti M, Rocha V, Verdot C, Mendes V, de Oliveira VLS, Braga AD, Martins VD, de Faria AMC, Amaral FA, Georgel P, Vieira AT, Muller S (2022). The therapeutic effect of phosphopeptide P140 attenuates inflammation induced by uric acid crystals in gout arthritis mouse model. Cells 11:3709. doi: 10.3390/cells11233709.
Thurner L, Fadle N, Regitz E, Preuss KD, Neumann F, Cetin O, Schormann C, Hoffmann MC, Herr C, Kheiroddin P, Rixecker TM, Bals R, Muller S, Thurner B, Kessel C, Kabesch M, Bewarder M, Heyne K, Lensch C, Kos IA (2022). Autoantibodies against SUMO1-DHX35 in long-COVID. J Transl Autoimmun 5:100171. doi: 10.1016/j.jtauto.2022.100171.
Akiyama K, Aung KT, Talamini L, Huck O, Kuboki T, Muller S (2022). Therapeutic effects of peptide P140 in a mouse periodontitis model. Cell Mol Life Sci 79:518. doi: 10.1007/s00018-022-04537-2.
Radic M, Muller S (2022). LL-37, a Multi-Faceted Amphipathic Peptide Involved in NETosis. Cells 11(15):2463. doi: 10.3390/cells11152463.
Schall N, Talamini L, Wilhelm M, Jouvin-Marche E, Muller S (2022). P140 peptide leads to clearance of autoreactive lymphocytes and normalizes immune response in lupus-prone mice. Front Immunol 13:904669. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.904669.
Retnakumar SV, Geesala R, Bretin A, Tourneur-Marsille J, Ogier-Denis E, Maretzky T, Nguyen HTT, Muller S (2022) Targeting the endo-lysosomal autophagy pathway to treat inflammatory bowel diseases. J Autoimmun128:102814. doi: 10.1016/j.jaut.2022.102814.
Gay N, van Gemert C, Merilles OE Jr, Georgel P (2022). Pacific island nations face an urgent need for actions and future research on COVID-19. Lancet Reg Health West Pac 18:100326. doi: 10.1016/j.lanwpc.2021.100326.
De Cauwer A, Loustau T, Erne W, Pichot A, Molitor A, Stemmelen T, Carapito R, Orend G, Bahram S, Georgel P (2022). Dicer1 deficient mice exhibit premature aging and metabolic perturbations in adipocytes. iScience 25(10):105149. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2022.105149.
Bonam SR, Tranchant C, Muller S (2021). Autophagy-Lysosomal Pathway as Potential Therapeutic Target in Parkinson’s Disease. Cells 10:3547. doi: 10.3390/cells10123547.
Schall N, Daubeuf F, Marsol C Frossard N, Bonnet D, Galzi JL, Muller S (2021). A selective neutraligand for CXCL12/SDF-1a with beneficial regulatory functions in MRL/lpr lupus prone mice. Front Pharmacol 12:752194. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.752194.
Daubeuf F, Schall N, Petit-Demoulière N, Frossard N, Muller S (2021). An autophagy modulator peptide prevents lung function decrease and corrects established inflammation in murine models of airway allergy. Cells 10:2468. doi: 10.3390/cells10092468.
Rafiq S, McKenna SL, Muller S, Tschan MP, Humbert M (2021). Lysosomes in acute myeloid leukemia: potential therapeutic targets? Leukemia. doi: 10.1038/s41375-021-01388-x.
Dotan A, Kanduc D, Muller S, Makatsariya A, Shoenfeld Y (2021). Molecular mimicry between SARS-CoV-2 and the female reproductive system. Am J Reprod Immunol 10.1111/aji.13494. doi: 10.1111/aji.13494.
Wilhelm M, Bonam SR, Schall N, Bendorius M, Korganow AA, Lumbroso C, Muller S (2021). Implication of a lysosomal antigen in the pathogenesis of lupus erythematosus. J Autoimmun 120:102633. doi: 10.1016/j.jaut.2021.102633.
Talamini L, Matsuura E, De Cola L, Muller S (2021). Immunologically inert nanostructures as selective therapeutic tools in inflammatory diseases. Cells 10(3):707. doi: 10.3390/cells10030707.
Klionsky DJ et al. (2021). Guidelines for the use and interpretation of assays for monitoring autophagy (4th edition). Autophagy 17:1-382. doi: 10.1080/15548627.2020.1797280.
Dotan A, Muller S, Kanduc D, David P, Halpert G, Shoenfeld Y (2021). The SARS-CoV-2 as an instrumental trigger of autoimmunity. Autoimmun Rev 20(4):102792. doi: 10.1016/j.autrev.2021.102792.
Mariotte A, Bernardi L, Macquin C, DeCauwer A, Kotova I, Blüml S, Noël D, Scanu A, Punzi L, Carapito C, Sibilia J, Bahram S, Georgel P (2021). NKG2D ligands in inflammatory joint diseases: analysis in human samples and mouse models. Clin Exp Rheumatol 39(5):982-987. doi: 10.55563/clinexprheumatol/klc3h6.
Nehmar R, Fauconnier L, Alves-Filho J, Togbe D, De Cauwer A, Bahram S, Le Bert M, Ryffel B, Georgel P (2021). Aryl hydrocarbon receptor (Ahr)-dependent Il-22 expression by type 3 innate lymphoid cells (ILC3) control of acute joint inflammation. J Cell Mol Med 25(10):4721-4731. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.16433.
Clere-Jehl R, Merdji H, Kassem M, Macquin C, De Cauwer A, Sibony A, Kurihara K, Minniti L, Abou Fayçal C, Bahram S, Meziani F, Helms J, Georgel P (2021). A Translational Investigation of IFN-α and STAT1 Signaling in Endothelial Cells during Septic Shock Provides Therapeutic Perspectives. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 65(2):167-175. doi: 10.1165/rcmb.2020-0401OC.
Lévy D, Mariotte A, DeCauwer A, Macquin C, Pichot A, Molitor A, Maurier F, Meyer A, Carapito R, Georgel P (2021). Contrasting role of NLRP12 in autoinflammation: evidence from a case report and mouse models. RMD Open 7(3):e001824. doi: 10.1136/rmdopen-2021-001824.
Georgel P (2021). Crosstalk between Interleukin-1β and Type I Interferons Signaling in Autoinflammatory Diseases. Cells10(5):1134. doi: 10.3390/cells10051134.
Georgel PT, Georgel P (2021). Where Epigenetics Meets Food Intake: Their Interaction in the Development/Severity of Gout and Therapeutic Perspectives. Front Immunol 12:752359. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.752359.
Bonam SR, Areti A, Komirishetty P, Muller S (2020). Dendrimers in immunotherapy and hormone therapy. In Pharmaceutical applications of dendrimers (Eds: Chauhan A, Kulhari H), chapter 10 pages 233-249. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-814527-2.00010-X.
Bonam SR, Muller S (2020). Parkinson’s disease is an autoimmune disease: a reappraisal. Autoimmun Rev 19(12):102684. doi: 10.1016/j.autrev.2020.102684.
Wang F, Tasset I, Cuervo AM, Muller S (2020). In vivo remodeling of altered autophagy-lysosomal pathway by a phosphopeptide in lupus. Cells 9(10):2328. doi: 10.3390/cells9102328.
Narasaraju T, Tang BM, Herrmann M, Muller S, Chow VTK, Radic M (2020). Neutrophilia and NETopathy as Key Pathologic Drivers of Progressive Lung Impairment in Patients With COVID-19. Front Pharmacol 11:870. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2020.00870.
Bonam SR, Muller S, Bayry J, Klionsky DJ (2020). Autophagy as an emerging target for COVID-19: lessons from an old friend, chloroquine. Autophagy 16(12):2260-2266. doi: 10.1080/15548627.2020.1779467.
Bonam SR, Tschan MP, Bayry J, Muller S (2020). Progress and challenges in the use of MAP1LC3 as a legitimate marker for measuring dynamic autophagy in vivo. Cells 9(5):1321. doi: 10.3390/cells9051321.
Voynova E, Lefebvre F, Qadri A, Muller S (2020). Correction of autophagy impairment inhibits pathology in the NOD.H-2h4 mouse model of primary Sjögren's syndrome. J Autoimmun 108:102418. doi: 10.1016/j.jaut.2020.102418.
Mariotte A, De Cauwer A, Po C, Abou-Faycal C, Pichot A, Paul N, Aouadi I, Carapito R, Frisch B, Macquin C, Chatelus E, Sibilia J, Armspach JP, Bahram S, Georgel P (2020). A mouse model of MSU-induced acute inflammation in vivo suggests imiquimod-dependent targeting of Il-1β as relevant therapy for gout patients. Theranostics 10(5):2158-2171. doi: 10.7150/thno.40650.
Kuchler-Bopp S*, Mariotte A, Strub M, Po C, De Cauwer A, Schulz G, Van Bellinghen X, Fioretti F, Clauss F, Georgel P*, Benkirane-Jessel N, Bornert F (2020). Temporomandibular joint damage in K/BxN arthritic mice. Int J Oral Sci 12(1):5. doi: 10.1038/s41368-019-0072-z.
Clere-Jehl R, Mariotte A, Meziani F, Bahram S, Georgel P*, Helms J* (2020). JAK-STAT Targeting Offers Novel Therapeutic Opportunities in Sepsis. Trends Mol Med 26(11):987-1002. doi: 10.1016/j.molmed.2020.06.007.
Bonam SR, Wang F, Muller S (2019). Lysosomes as a therapeutic target. Nat Rev Drug Discovery 18:923-948. doi: 10.1038/s41573-019-0036-1.
Bonam SR, Ruff M, Muller S (2019). HSPA8/HSC70 in Immune Disorders: A Molecular Rheostat that Adjusts Chaperone-Mediated Autophagy Substrates. Cells 8:849. doi: 10.3390/cells8080849.
Bonam SR, Bhunia D, Muller S, Nerella SG, Alvala M, Halmuthur Mahabalarao SK (2019). Novel trisaccharide based phospholipids as immunomodulators. Int Immunopharmacol 74:105684. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2019.105684.
Retnakumar SV, Muller S (2019). Pharmacological Autophagy Regulators as Therapeutic Agents for Inflammatory Bowel Diseases. Trends Mol Med 25:516-537. doi: 10.1016/j.molmed.2019.03.002.
Arbogast F, Arnold J, Hammann P, Kuhn L, Chicher J, Murera D, Weishaar J, Muller S, Fauny JD, Gros F (2019). ATG5 is required for B cell polarization and presentation of particulate antigens. Autophagy 15:280-294. doi: 10.1080/15548627.2018.1516327.
Wang F, Bonam SR, Schall N, Kuhn L, Hammann P, Chaloin O, Madinier JB, Briand JP, Page N, Muller S (2018). Blocking nuclear export of HSPA8 after heat shock stress severely alters cell survival. Sci Rep 8:16820. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-34887-6.
Bendorius M, Po C, Muller S, Jeltsch-David H (2018). From systemic inflammation to neuroinflammation: the case of neurolupus. Int J Mol Sci 19:3588. doi: 10.3390/ijms19113588.
Bendorius M, Neeli I, Wang F, Bonam SR, Dombi E, Buron N, Borgne-Sanchez A, Poulton J, Radic M, Muller S (2018). The mitochondrion-lysosome axis in adaptive and innate immunity: Effect of lupus regulator peptide P140 on mitochondria autophagy and NETosis. Front Immunol 9:2158. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.02158.
Bonam SR, Wang F, Muller S (2018). Autophagy: A new concept in autoimmunity regulation and a novel therapeutic option. J Autoimmun 94:16-32. doi: 10.1016/j.jaut.2018.08.009.
Muller S (2018). Excipients: not so inert? When the excipient plays the role of an active substance, as exemplified by systemic lupus. Swiss Med Wkly 148:w14631. doi: 10.4414/smw.2018.14631.
Bonam SR, Wu YS, Tunki L, Chellian R, Kumar Halmuthur MS, Muller S, and Pandy V (2018). What Has Come out from Phytomedicines and Herbal Edibles for the Treatment of Cancer? ChemMedChem 13:1854-1872. doi: 10.1002/cmdc.201800343.
Brun S, Schall N, Bonam SR, Bigauta K, Mensah-Nyagana AG, de Sèze J, Muller S (2018). An autophagy-targeting peptide to treat chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathies. J Autoimmun 92:114-125. doi: 10.1016/j.jaut.2018.05.009.
Murera D, Arbogast F, Arnold J, Bouis D, Muller S, Gros F (2018). CD4 T cell autophagy is integral to memory maintenance. Sci Rep 8:5951. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-23993-0.
Wilhelm M, Wang F, Schall N, Kleinmann JF, Faludi M, Nashi EP, Sibilia J, Martin T, Schaeffer E, Muller S (2018). Lupus regulator peptide P140 represses B-cell antigen differentiation by reducing HLA class II overexpression. Arthritis Rheumatol 70:1077-1088. doi: 10.1002/art.40470.
Bermúdez M, Arévalo-Pinzón G, Rubio L, Chaloin O, Muller S, Curtidor H, Patarroyo MA (2018). Receptor-ligand and parasite protein-protein interactions in Plasmodium vivax: Analysing rhoptry neck proteins 2 and 4. Cell Microbiol 20(7):e12835. doi: 10.1111/cmi.12835.
Li B, Wang F, Schall N, Muller S (2018). Rescue of autophagy and lysosome defects in salivary glands of MRL/lpr mice by a therapeutic phosphopeptide. J Autoimmun 90:132-145. doi: 10.1016/j.jaut.2018.02.005.
Kökten T, Gibot S, Lepage P, D'Alessio S, Hablot J, Ndiaye NC, Busby-Venner H, Monot C, Garnier B, Moulin D, Jouzeau JY, Hansmannel F, Danese S, Guéant JL, Muller S, Peyrin-Biroulet L (2018). TREM-1 Inhibition Restores Impaired Autophagy Activity and Reduces Colitis in Mice. J Crohns Colitis 12(2):230-244. doi: 10.1093/ecco-jcc/jjx129.

