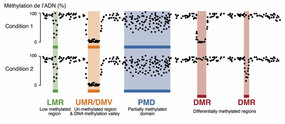
DNA methylation is an epigenetic modification that represses gene expression. In an article published in Nucleic Acids Research, scientists from the IGBMC and Michaël Weber's team "Epigenetic Regulation of Cellular Identity" describe a new bioinformatics method for analyzing DNA methylation data at the genome level. This approach is useful for better understanding DNA methylation changes induced in different physiological or pathological conditions.
High-throughput sequencing approaches now make it possible to map DNA methylation levels across the entire genome. However, the development of bioinformatics methods is still necessary to analyze the data and extract the maximum amount of information.
The scientists have developed an innovative method called MethyLasso that allows for fine-grained analysis of DNA methylation data. This approach first performs a segmentation of the data in order to identify regions of the genome that are demethylated and that correspond to active regulatory regions bound by transcription factors. MethyLasso also makes it possible to identify differentially methylated regions between two conditions, such as between healthy and cancerous cells.
The new MethyLasso tool therefore allows scientists studying DNA methylation to carry out a detailed analysis of the data in order to better characterize the deregulations observed in different pathological conditions.
For more information, read the news published by the CNRS Biology.
Article :
Balaramane D, Spill YG, Weber M*, Bardet AF* (2024). MethyLasso: a segmentation approach to analyze DNA methylation patterns and identify differentially methylated regions from whole-genome datasets. Nucleic Acids Res 18:gkae880. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkae880.